Development and testing of self-deformed composites
- Published in Research
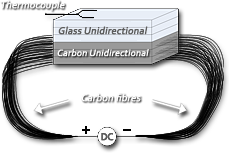 A multifunctional composite without insertion of actuators can be developed by exploiting the thermal anisotropy of a composite laminate in order to induce shape changes by internal heating. Indeed a selective thermal activation of one or more layers inside the material would create thermal stresses, which could induce shape change to the material at the macroscopic level, just as those observed in the bimetallic strips.
A multifunctional composite without insertion of actuators can be developed by exploiting the thermal anisotropy of a composite laminate in order to induce shape changes by internal heating. Indeed a selective thermal activation of one or more layers inside the material would create thermal stresses, which could induce shape change to the material at the macroscopic level, just as those observed in the bimetallic strips.

 Modern technologies need
Modern technologies need 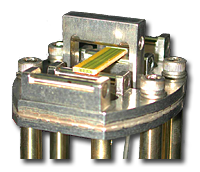 The integration of
The integration of 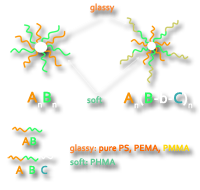 Block copolymers are excellent candidates for a
Block copolymers are excellent candidates for a